Types Of Heat Loss In The Integumentary System
Use of body heat to convert liquid water in sweat to gaseous water vapor. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
 7 Facts About The Integumentary System Every Nursing Student Should Know Nursecepts
7 Facts About The Integumentary System Every Nursing Student Should Know Nursecepts
Skin damaged by burns is less effective at preventing fluid loss often resulting in a possibly life threatening problem if not treated.

Types of heat loss in the integumentary system. The first is a. Blister Third degree - full thickness destroying epidermis dermis part of hypodermis. Air currents can increase evaporative heat loss through convection.
The integumentary system functions in thermoregulationthe ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundarieseven when the surrounding temperature is very different. 13 Loss of sensory receptors in the skin affects sensitivity to touch temperature and pain making the elder more susceptible to cuts abrasions and burns. The integumentary system is composed primarily of the skin and accessory.
The evaporation of the sweat from the surface of the skin cools the body by dissipating heat. The integumentary system is supplied by the cutaneous circulation which is crucial for thermoregulation. This reduced circulation can result in the skin taking on a whitish hue.
Skin and Sensory Reception Back to Top. The loss of heat from a warm body to a cooler object in contact with the warm body - sitting on ice block. Loss of heat by air currents moving over the surface of the skin - fan moves air across skin constantly removing layer of heated air next to the body.
A burn results when the skin is damaged by intense heat radiation electricity or chemicals. There are four types of glands in the integumentary system. Type of Heat Loss 1.
The skin provides an overlaying protective barrier from the environment and pathogens while contributing to the adaptive immune system. When the core body temperature drops the body switches to heat-conservation mode. It consists of three types.
Catastrophic loss of body fluids Dehydration and fatal circulatory shock Infection Types First degree epidermis. Two other cell types are found dispersed among the basal cells in the stratum basale. Epithelial cells secrete mucous shells and exoskeletons made of chitin stinging or sharp outer shells Jellyfish Insects Worms.
Sudoriferous sweat glands sebaceous glands ceruminous glands and mammary glands. The human integumentary system is an external body covering but also much more. Water loss occurs in the skin by two routes.
The damage results in the death of skin cells which can lead to a massive loss of fluid. The direct cutaneous are derived directly from the main arterial trunks and drain into the main venous vessels. Sudoriferous glands are sweat producing glands.
The sympathetic nervous system is continuously monitoring body temperature and initiating appropriate motor responses. INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM The skin and associated structures make up the integumentary system. The integumentary system helps regulate body temperature through its tight association with the sympathetic nervous system the division of the nervous system involved in our fight-or-flight responses.
What type of integumentary system do invertebrates have. Although the temperature of the skin drops as a result passive heat loss is prevented and internal organs and structures remain warm. This process is one aspect of homeostasis.
Functions of the Integumentary System. These changes in sensory receptors are also responsible for an increase in pain threshold and impaired pain localization in elders and as in the case of injury to the skin can. Describe the integumentary system and the role it plays in homeostasis.
Without it an individual would be attacked immediately by bacteria and die from heat and water loss. Walls of dermal blood vessels are stimulated to contract decreasing flow of heat-carrying blood through skin reducing heat loss and sweat glands remain inactive nervous system stimulates muscles to contract. This can include an inhibition to excessive sweating and a decrease of blood flow to the papillary layers of the skin.
These are important to help maintain body temperature. Skin is a mammals largest organ. When body temperatures drop the arterioles constrict to minimize heat loss particularly in the ends of the digits and tip of the nose.
Heat transfer occurs in a gas or liquid by the circulation of currents from 1 region to another. Heat is carried away by movement of air over surface. Sunburn Second degree epidermis and upper dermis.
It is absolutely essential to life. These are all exocrine glands secreting materials outside the cells and body. Dehydration electrolyte imbalance and renal and circulatory failure follow which can be fatal.
Direct cutaneous musculocutaneous and fasciocutaneous systems. Heat is emitted in waves rays from warmer surfaces to cooler surroundings. This reduction of blood flow helps conserve body heat.
Heat molecular vibration is transmitted from one substance directly to another. In hot weather up to 4 liters per hour can be lost by these mechanisms. A dynamic state of stability between an animals internal and external environment.
Inefficient temperature regulation as a result of the reduction in sweat glands and loss of fatty tissue increases the risk of heat stroke in the aged. The blood vessels expand bringing hot blood to the surface to increase heat loss. Start studying Integumentary System Test Questions.
Its protects the body against physical chemical and biological attacks it helps to regulate body. This is the heat loss responsible for windchill factor. Heat is lost as perspiration or other fluids on skin.
It protects nourishes insulates and cushions. The skin protects land-dwelling organisms from desiccation and from loss of heat. This stored fat can serve as an energy reserve insulate the body to prevent heat loss and act as a cushion to protect underlying structures from trauma.
Blood Supply to the Epidermis.
 7 Facts About The Integumentary System Every Nursing Student Should Know Nursecepts
7 Facts About The Integumentary System Every Nursing Student Should Know Nursecepts
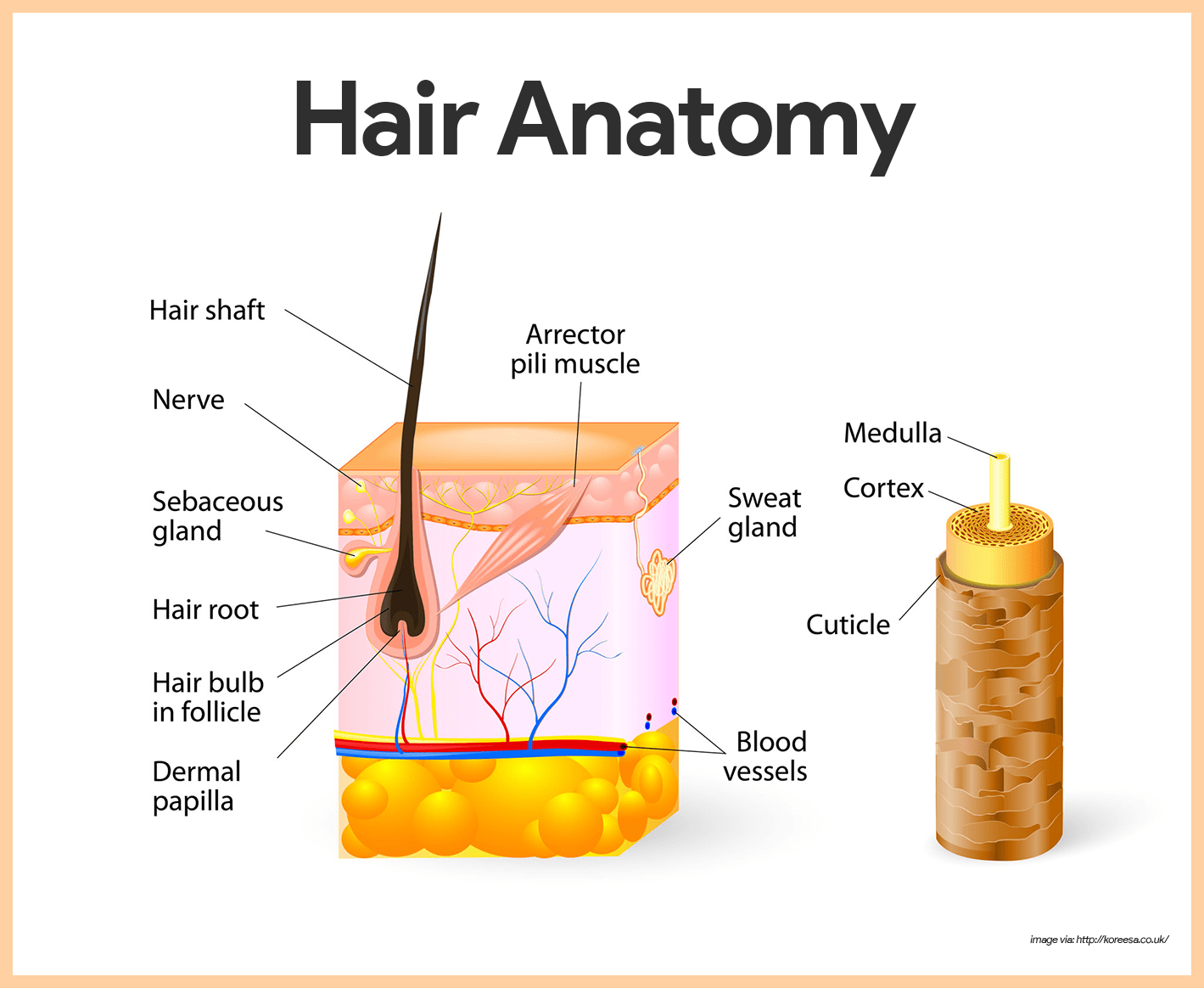 Integumentary System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Integumentary System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Ch 5 Integumentary System Flashcards Quizlet
Ch 5 Integumentary System Flashcards Quizlet
 Integumentary System Quiz Free At Quizzma
Integumentary System Quiz Free At Quizzma
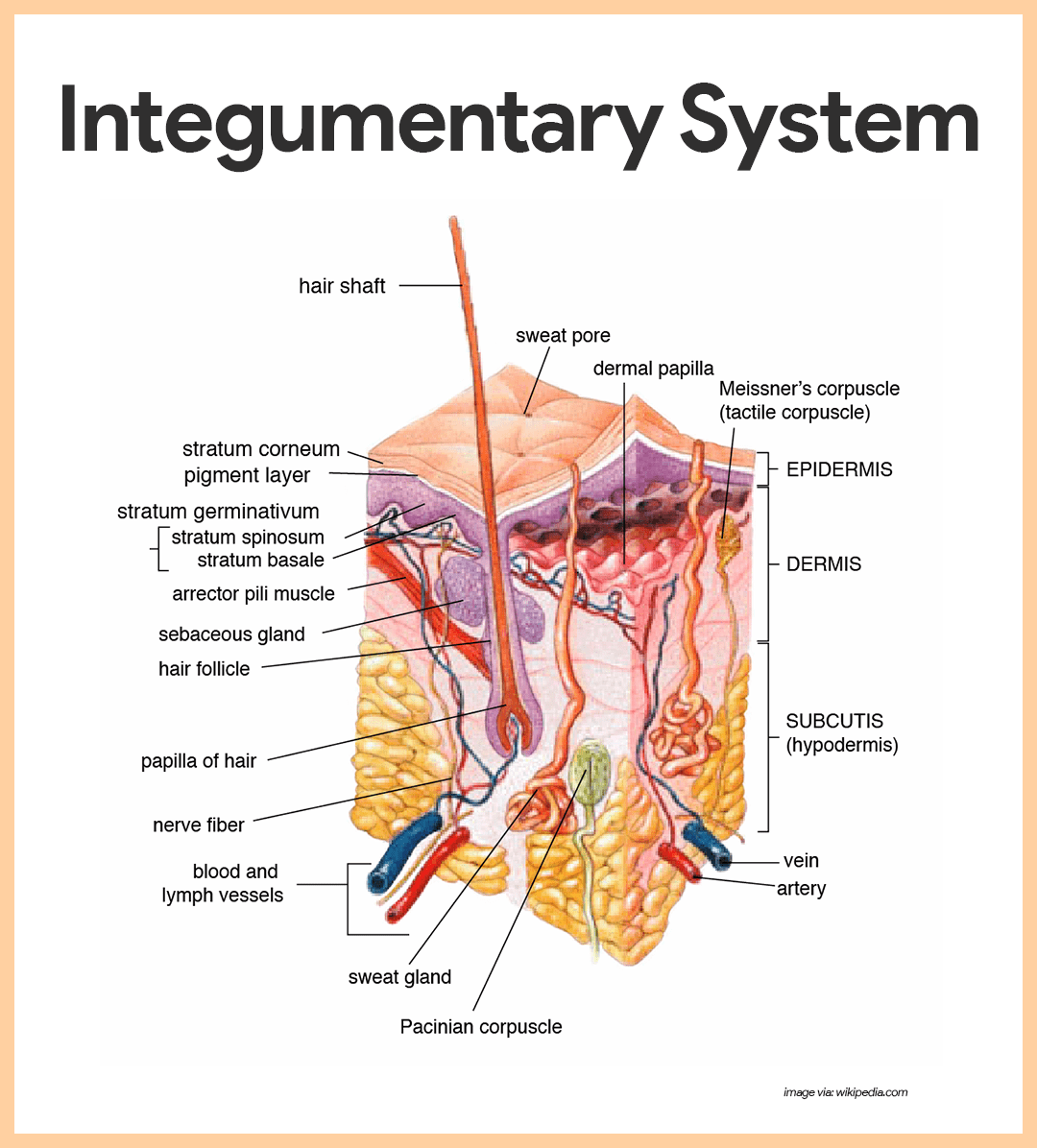 Integumentary System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Integumentary System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
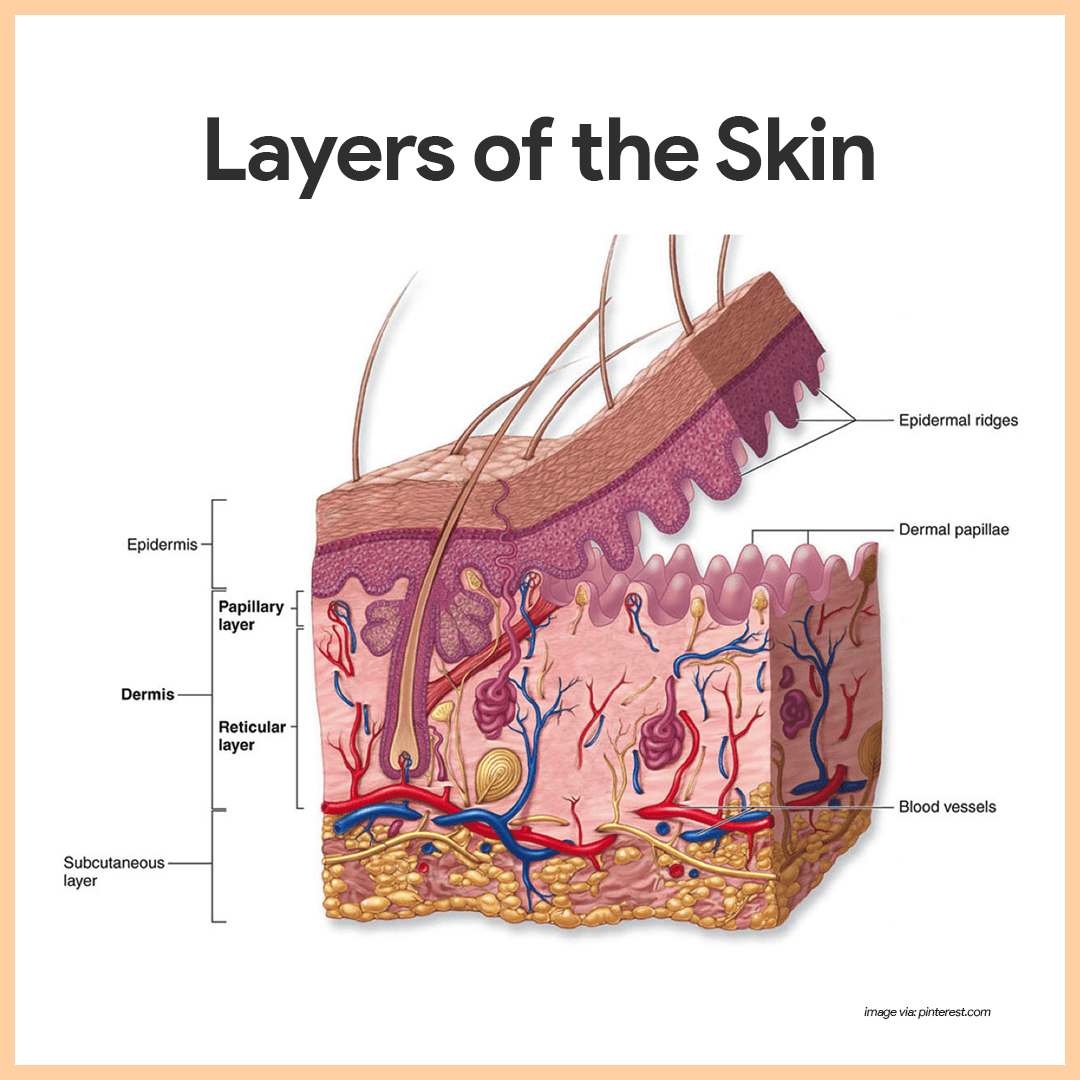 Integumentary System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Integumentary System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
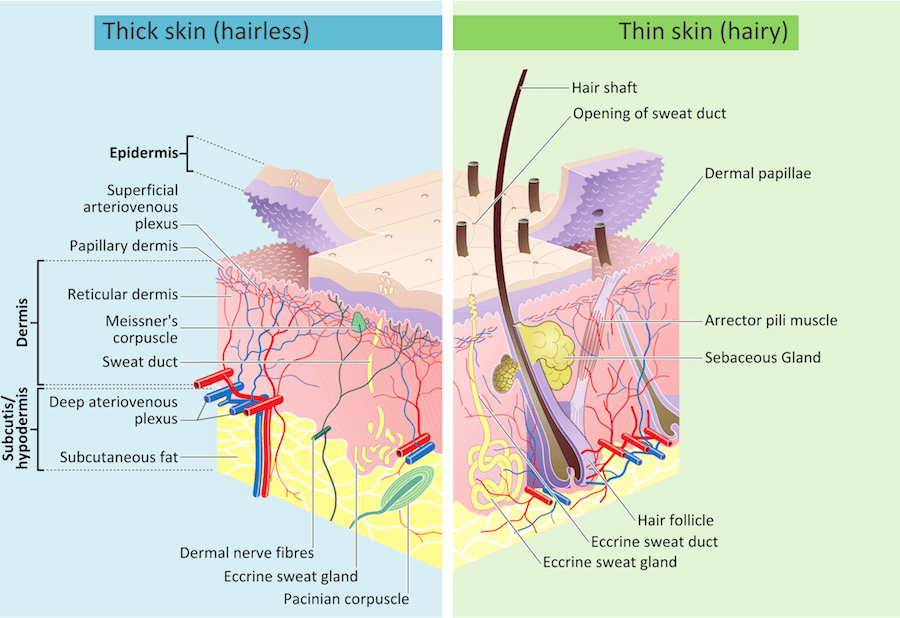 Pacific Medical Training Integumentary System
Pacific Medical Training Integumentary System
 Lab 6 The Skin Integumentary System Flashcards Quizlet
Lab 6 The Skin Integumentary System Flashcards Quizlet
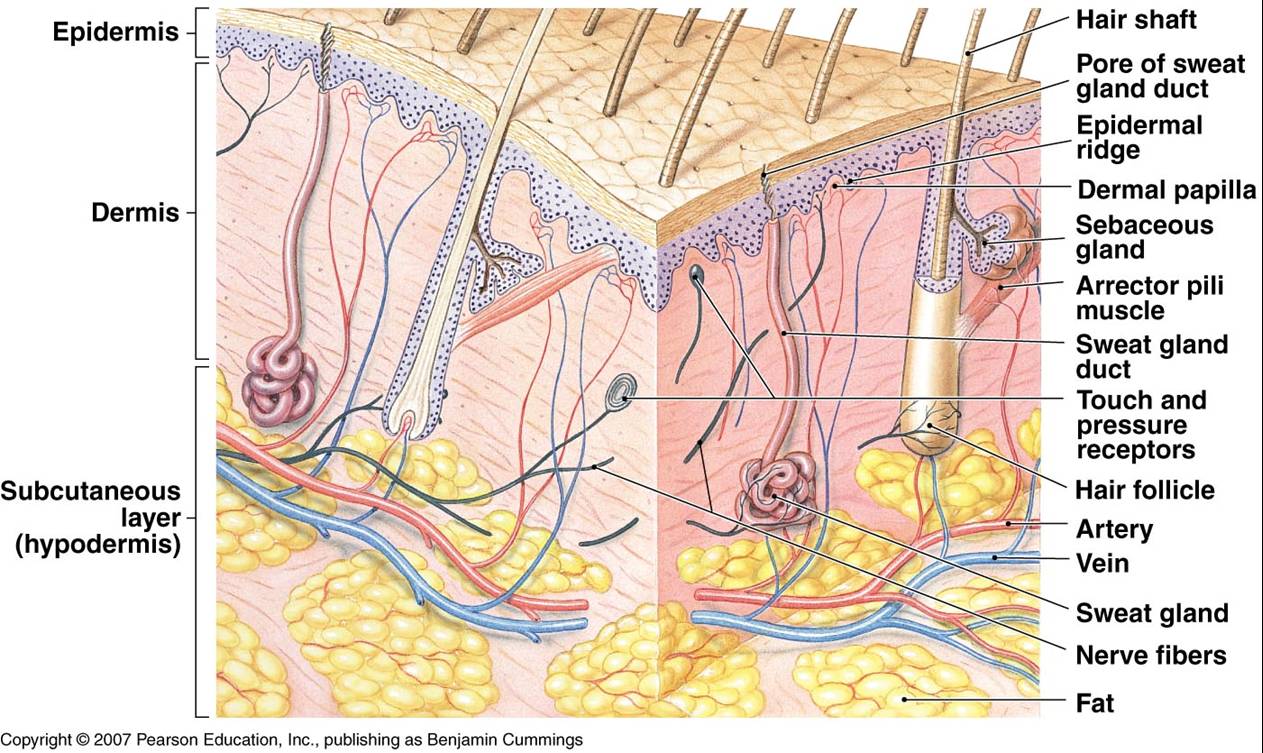 Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review
Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review
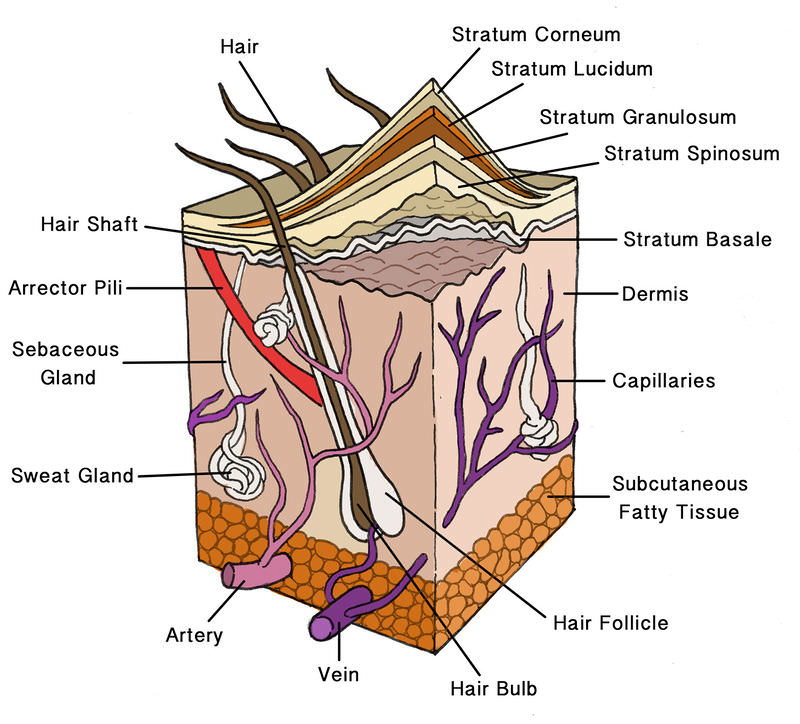
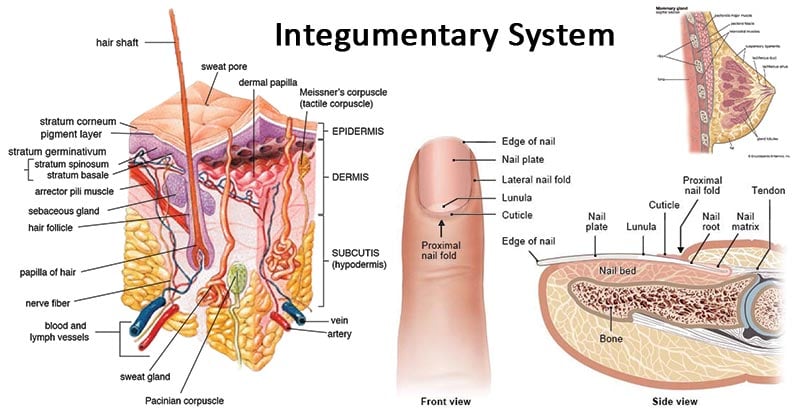 Integumentary System Definition Organs Functions Diseases
Integumentary System Definition Organs Functions Diseases
 Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Mblex Review Integumentary System Anatomy And Physiology Mblexguide
Mblex Review Integumentary System Anatomy And Physiology Mblexguide
 Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Functions Of The Integumentary System Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
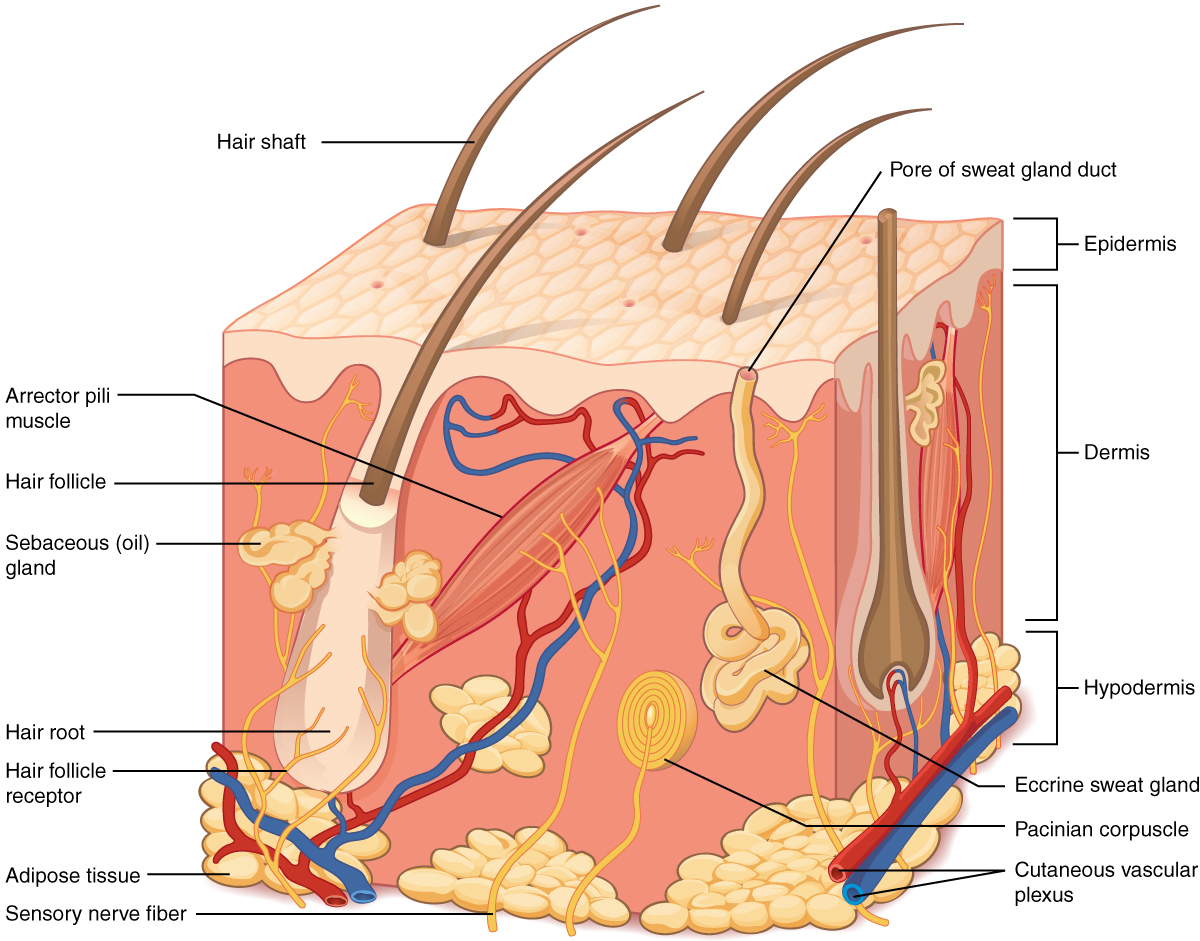 Integumentary System Biology For Majors Ii
Integumentary System Biology For Majors Ii